Properties
Definition of a Function
A function takes an input x and outputs a value y.
Domain
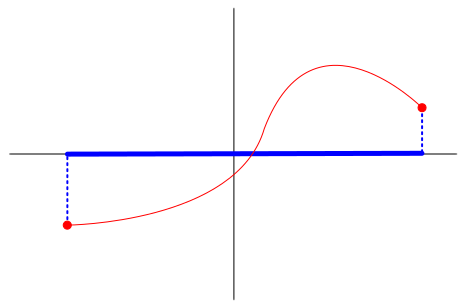
The domain describes all possible values x that a function can take as an input.
Range
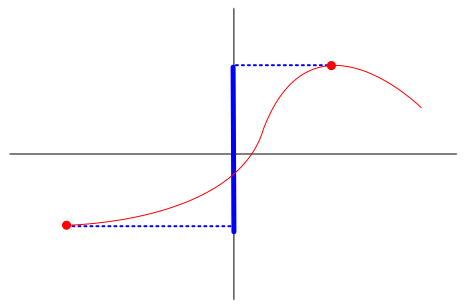
The range describes all the possible values f(x) that a function can output.
Vertical Line Test
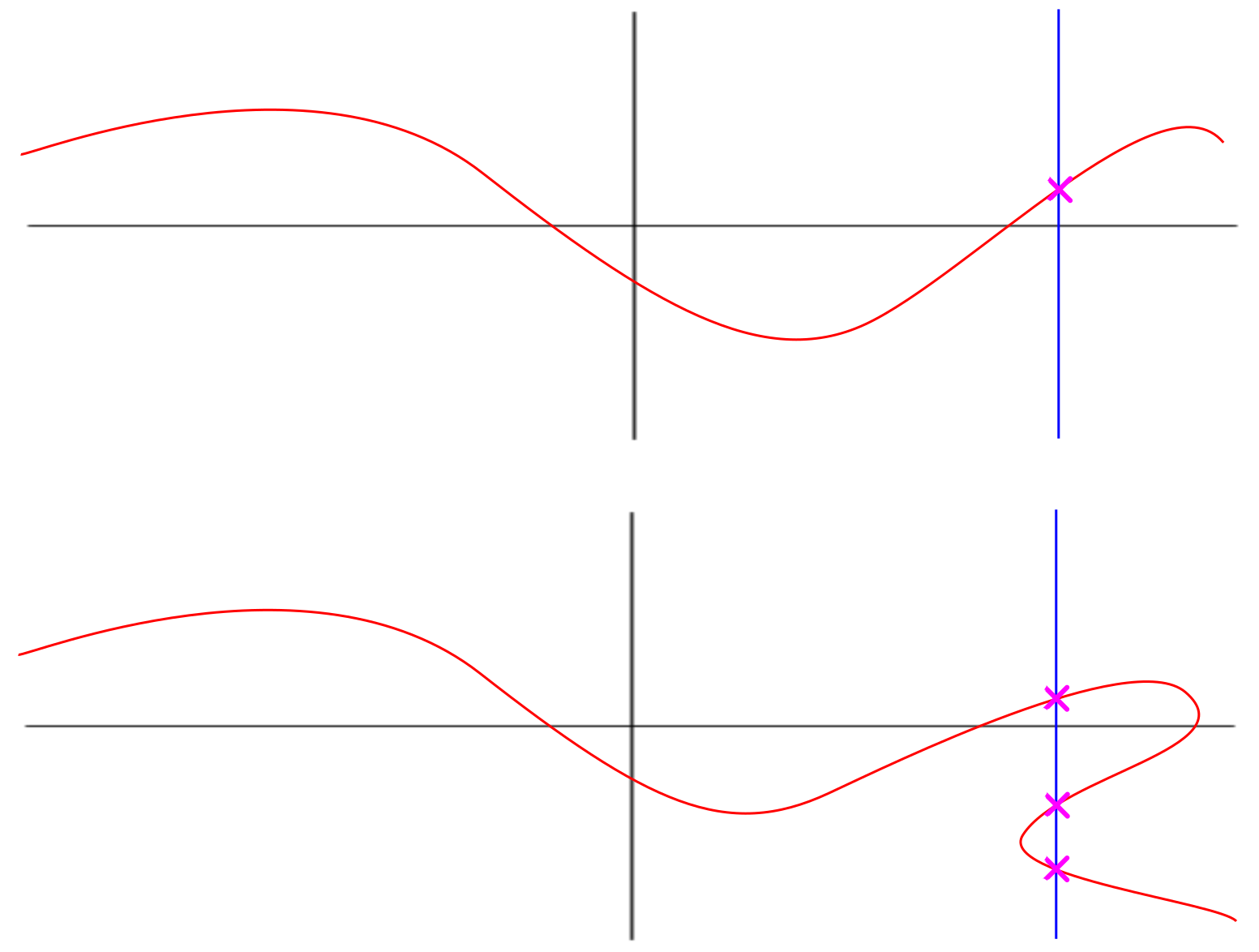
The graph of a valid function only touches a vertical line once anywhere in its domain.
Even Functions
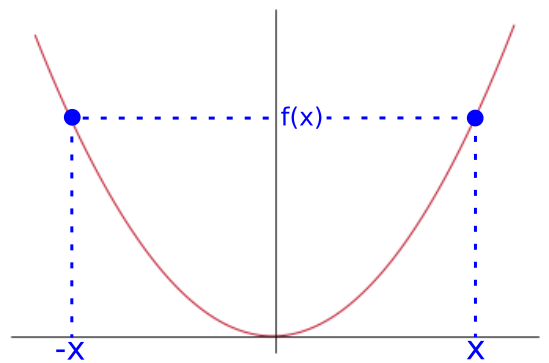
An even function is a function such that f(-x)=f(x). Visually this is a function that is reflected across the y-axis.
Odd Functions
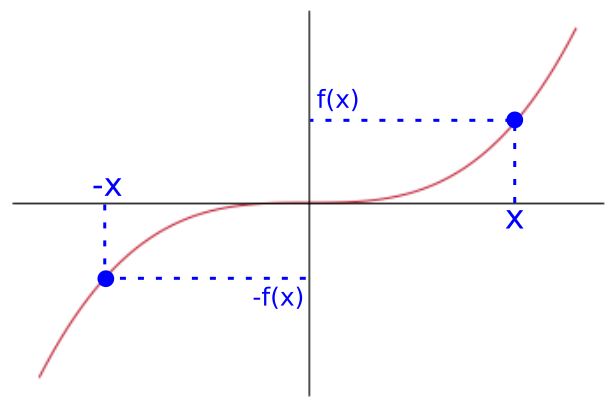
An odd function is a function such that f(-x)=-f(x). Visually this is a function that is reflected across the origin.
Increasing Functions
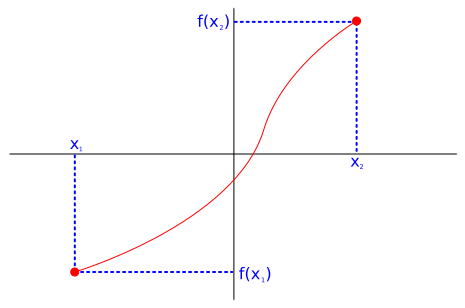
A function is increasing in range if for every value x1<x2, f(x2)>f(x1).
Decreasing Functions
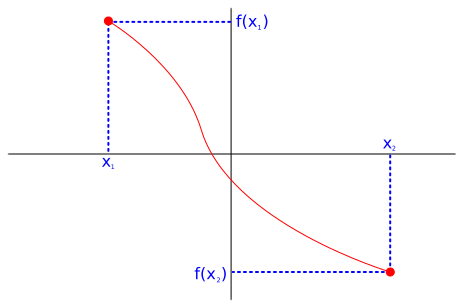
A function is decreasing in range if for every value x1<x2, f(x1)>f(x2).
Inverse Function
The inverse function takes the dependent variable from the original function and returns the independent variable. The range of a function is the domain of its inverse and vice versa.
Composition of Functions
The composition "f of g" means that x is first put through the function g(x), then the output of that is put through the function f(x).
Inverse Function Composition
The inverse of a function is a function that it completely reverses the effects of another function when the two are composed together throughout a specified range.
Function Operations
One-to-One Function
A function is one-to-one if and only if it does not output the same value for two separate inputs. A function must be one-to-one within a specified range for it to have an inverse.
Horizontal Line Test
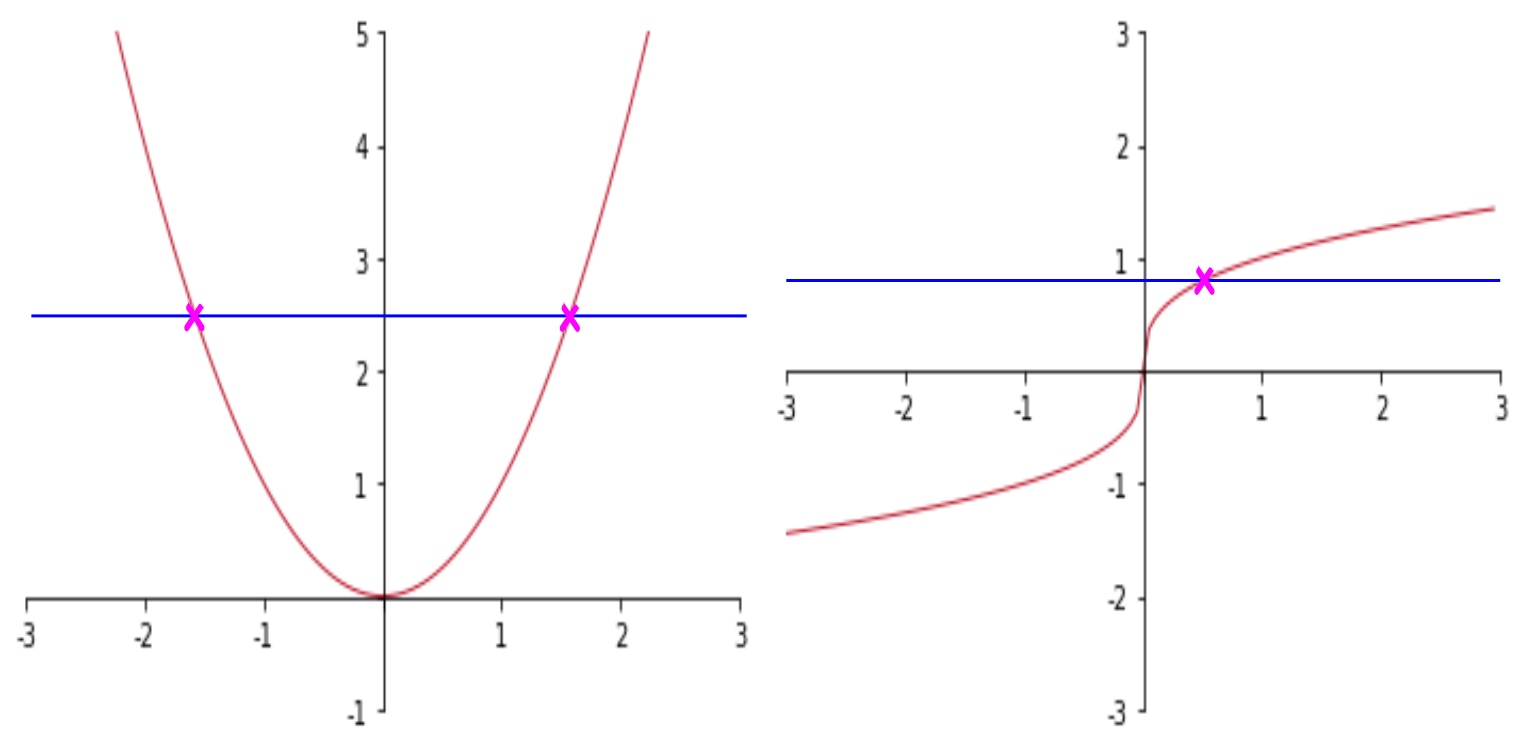
A function is one-to-one within a range if its graph does not touch a horizontal line more than once along its range.
Transformations
Function
.png)
Vertical Translation (Up)
+3.png)
Vertical Translation (Down)
-3.png)
Horizontal Translation (Left)
.png)
Horizontal Translation (Right)
.png)
Vertical Scaling (Squash)
_div_3.png)
Vertical Scaling (Pull)
_mul_3.png)
Horizontal Scaling (Squash)
.png)
Horizontal Scaling (Pull)
.png)